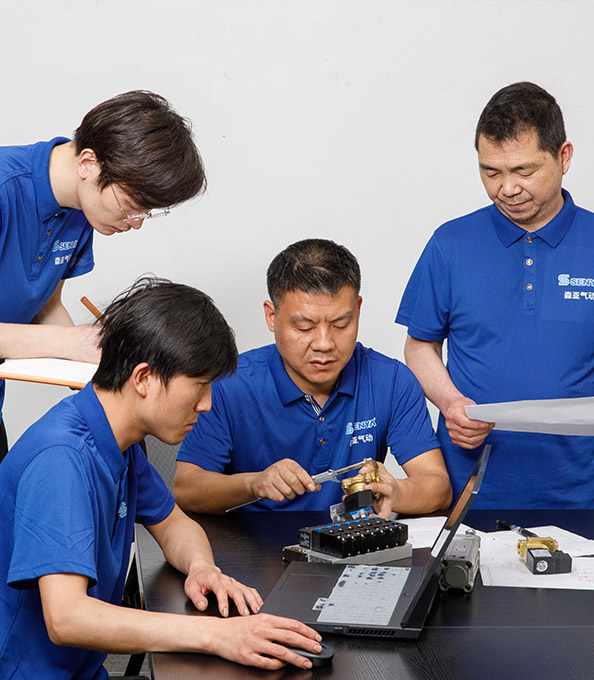
Professional manufacturer of pneumatic components for over decades
We have focused on producing valves, cylinders, and other pneumatic-related products with a high brand reputation and rich industrial application experience.
Commitment To Superior Quality
Recent News
-
How to maintain and care for pneumatic cylinders to extend their service life?
Pneumatic cylinders are common power actuators in industrial automation and mechanical equipment. In order to ensure the efficient operation of pneuma...
-
How to improve the response speed of the solenoid valve to meet the application requirements of fast start and stop?
Improving the response speed of solenoid valves is an important task to meet the needs of fast start-stop applications. Solenoid valves are widely use...
-
In practical applications, which industries need to use air filter regulators the most and why?
Air filter regulators play a vital role in many industries, especially in areas where the air quality and pressure of pneumatic systems are extremely ...
-
How does a 2/2 channel brass solenoid valve work and how does it control fluid flow?
A 2/2 channel brass solenoid valve is a control valve widely used in pneumatic and hydraulic systems. Its main function is to regulate the flow of flu...
-
What are the main functions of pneumatic directional valve?
Pneumatic Directional Valves is an indispensable component of the pneumatic system. It is mainly used to control the gas flow direction and flow, ther...
-
How does the corrosion resistance of cast aluminum materials in pulse valves improve their service life in harsh environments?
As a vital component of industrial dust removal equipment, pulse valves often need to work in harsh environments, such as high temperature, high humid...
-
How do integrated filters and pressure regulators simplify compressed air management and provide a one-stop solution?
In modern industry, compressed air systems play a vital role. Whether it is used for pneumatic tools, production lines or automation systems, a stable...
-
What are the benefits of pilot design of solenoid valves?
The pilot design of solenoid valves is particularly beneficial in scenarios with low power and high flow requirements for the following reasons: 1. Hi...
-
How to maintain and service a solenoid valve with a high protection level to ensure its continued high performance after long-term use?
1. Professional maintenanceFor solenoid valves with high protection levels, professional maintenance services are the key to ensuring their long-term ...
-
How do high-flow designs and direct-acting structures work together to achieve efficient water flow control?
Faced with the ever-changing fire situation in firefighting scenes, a fast and sufficient water supply is the key to extinguishing fires. The 2WM seri...

 简体中文
简体中文 English
English Русский
Русский